Survival Kit:
It is ideal to have at least one survival pack near the entrance of your home, in your car, and inside your workplace. Place it in an easy-to-reach location and should at least contain the following:
- Non-perishable or no-prep meals (canned goods, crackers, cereal, canned juices)
- First Aid Kit (4×4 gauze pads, 8×10 gauze pads, adhesive bandages, gauze roller bandages, scissors, blanket, tweezers, adhesive tape, would cleaning agent, latex gloves, splint, aspirin, cold pack, antibiotic ointment, thermometer, safety pins)
- Clothes (undergarments, rubber shoes, slippers, t-shirt, jacket, lounge pants)
- Toiletries (bath soap, sanitary pads, toothbrush, toothpaste, insect repellant)
- Important Documents (passports, birth certificate)
- Essential Tools (whistle, lights/matches, flashlight, batteries, battery-powered radio, fully-charged power bank, extra cash, multi-purpose knife, extension cords)
Before an earthquake:
Take some time to prepare yourself, and your loved ones for a possible earthquake. As one can hit at any given time, being prepared with the necessary tools will likely ease your nerves in the midst of the calamity.
- Familiarize yourself with the location of fire extinguishers, medical kits, exit routes, and your building’s evacuation plan
- Have necessary house repairs fixed to avoid further damage
- Store harmful chemicals and flammable materials properly
- Secure heavy furniture and hanging objects
- Prepare your survival kit* (preferably one in your house, car, and workplace)
- Participate in office and community earthquake drills
- Discuss a designated meet up location with family in case you’re separated
- Learn simple first aid techniques
During an earthquake:
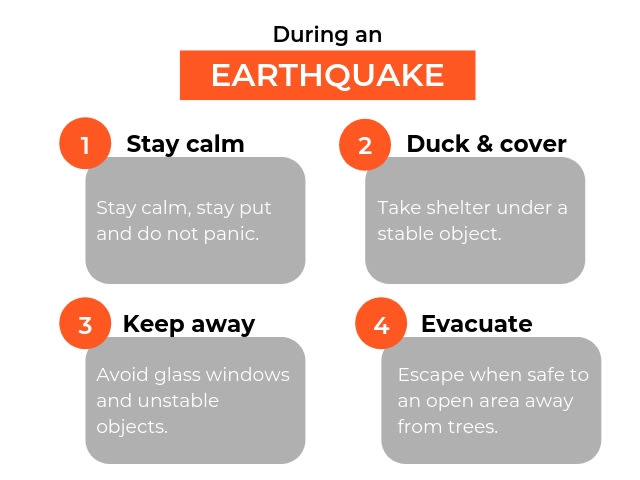
- Stay calm and stay put
- Duck, cover and hold under somewhere stable (ex. desk or table)
- Stay away from glass windows, shelves, and heavy and hanging objects
- Exit the building only once shaking stops via stairs. Elevators are not to be used.
- Evacuate to an open area away from trees, electric posts and landslide prone areas
- If you’re in a moving vehicle, step out and move towards a safer area.
- Avoid overpasses, slowly stop in an open area, and remain in your vehicle
After an earthquake:
- Stay alert in the event of aftershocks
- Check yourself and those in your surroundings are injuries and provide first aid. Prioritize children, pregnant women, PWDs, and senior citizens*
- For coastal locations, evacuate to higher ground immediately
- Double check for toxic spills and flammable chemicals
- Stay out of buildings until advised
- Check for water, electrical, gas, or LPG leaks and damages
- Stay updated through a battery-operated radio
- If signal is not down, message loved ones of your state and where you are
Emergency Apps

Although it is impossible to be alerted before an earthquake strikes, you may rely on the following emergency apps for earthquake detection. Apple users may also turn on their emergency and government alerts on their phone.
- Weather PH
- Quakefeed
- Batingaw
- Typhoon Tracker
- Firechat
- FEMA
- WEBSAFE
Retrieved From:
Felicia Dei on April 23, 2019